Dogs’ brains are sensitive to the familiar high-pitched “cute” voice tone that adult humans, especially women, use to talk to babies, according to a new study.
The research, published recently in the journal Communications Biology, found “exciting similarities” between infant and dog brains during the processing of speech with such a high-pitched tone feature.
Humans tend to speak with a specific speech style characterised by exaggerated prosody, or patterns of stress and intonation in a language, when communicating with individuals having limited language competence.
Such speech has previously been found to be very important for the healthy cognitive, social and language development of children, who are also tuned to such a high-pitched voice.
But researchers, including those from the Eötvös Loránd University in Hungary, hoped to assess whether dog brains are also sensitive to this way of communication.
In the study, conscious family dogs were made to listen to dog, infant and adult-directed speech recorded from 12 women and men in real-life interactions.
As the dogs listened, their brain activities were measured using a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan.
The study found the sound-processing regions of the dogs’ brains responded more to dog- and infant-directed than adult-directed speech.
This marked the first neurological evidence that dog brains are tuned to speech directed specifically at them.
“Studying how dog brains process dog-directed speech is exciting, because it can help us understand how exaggerated prosody contributes to efficient speech processing in a nonhuman species skilled at relying on different speech cues,” explained Anna Gergely, co-first author of the study.
Scientists also found dog- and infant-directed speech sensitivity of dog brains was more pronounced when the speakers were women, and was affected by voice pitch and its variation.
These findings suggest the way we speak to dogs matters, and that their brain is specifically sensitive to the higher-pitched voice tone typical to the female voice.
“Remarkably, the voice tone patterns characterizing women’s dog-directed speech are not typically used in dog-dog communication – our results may thus serve evidence for a neural preference that dogs developed during their domestication,” said Anna Gábor, co-first author of the study.
“Dog brains’ increased sensitivity to dog-directed speech spoken by women specifically may be due to the fact that women more often speak to dogs with exaggerated prosody than men,” Dr Gabor said.

Little Pup was abandoned, forced to endure a string of sorrowful days. Today, he has transformed into an exceptionally friendly companion
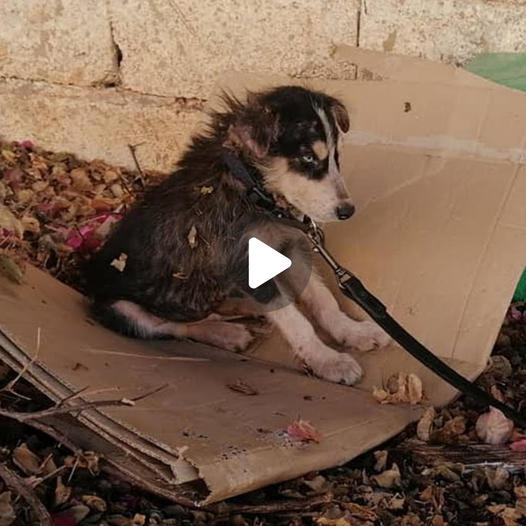

In a world the place compassion and kindness are important, the story of just a little pet’s transformation from a distressed and confined existence to changing into an extremely resilient and succesful member of society is a testomony to the facility of affection and care. This heartwarming story highlights the resilience and capability for change that resides inside each dwelling being.
The journey begins with a small pet, as soon as stuffed with innocence and curiosity, who discovered itself trapped by the tough chains of confinement. Days become weeks, and fear settled within the hearts of those that encountered this unlucky creature. The pet’s eyes, as soon as full of hope and vitality, held a glimmer of disappointment, as if it had misplaced all religion on the planet.
Nonetheless, as destiny would have it, a collection of lucky occasions unfolded, bringing a ray of sunshine into the pet’s life. A form-hearted particular person, pushed by empathy and a need to make a distinction, found the pet’s plight. Decided to offer an escape and an opportunity at a greater life, they set out on a mission to liberate the toddler from its confinement and provide it an opportunity at a greater life.
With cautious dedication, the chains that had shackled the pet to its previous have been regularly eliminated. Step-by-step, the pet started to emerge from its cocoon of isolation and provide its loyalty and friendship to the world. The pet’s eyes, now full of hope and vitality as soon as once more, shone as if it had rediscovered the enjoyment of life. The toll of its restrictive life-style had been evident, because it struggled to search out consolation on the planet it had been denied for thus lengthy.
Nonetheless, as destiny would have it, a collection of lucky occasions unfolded, bringing a ray of sunshine into the pet’s life. A form-hearted particular person, pushed by empathy and a need to make a distinction, found the pet’s plight. Decided to offer an escape and an opportunity at a greater life, they set out on a mission to liberate the toddler from its confinement and provide it an opportunity at a greater life.
With care and dedication, the chains that had sure the pet to its previous have been regularly eliminated. Step-by-step, the pet started to emerge from its cocoon of isolation and prolong its belief to others. The pet’s eyes, now full of hope and vitality as soon as once more, gleamed as if it had rediscovered the enjoyment of life. The journey of its outstanding transformation had simply begun.
Within the days that adopted, the pet was immersed in an atmosphere full of love, persistence, and understanding. It was showered with light touches, soothing phrases, and nourishing meals. The pet’s once-downtrodden spirit started to blossom, forging deep emotional connections with the individuals round it.
The transformation of this little pet serves as a reminder that each dwelling being has the potential to beat adversity and thrive. It’s a testomony to the facility of compassion and the profound affect it will probably have on a person’s life. Let this story encourage us to be sort, empathetic, and responsive caretakers of all creatures, making certain that they too have the chance to flourish on this world.


Leave a Reply