
For the person suffering from dementia as well as the ones closest to them, it may be an extremely frightening disease. On the other hand, early detection of dementia symptoms might make everyone feel better prepared. More equipped to handle the ambiguity, emotional upheaval, or perplexity. Fortunately, Dr. Richard Restak’s book, How to Prevent Dementia, was released on October 17, 2023. Some early indicators of the condition are covered in the book. The physician reveals in the book that there are four main dementia early warning indicators. He refers to the symptoms of dementia as the “Four A’s” and describes how they might manifest in routine activities like brushing your teeth. He stated that the exterior manifestations and internal feelings of an Alzheimer’s patient are driven by four deficits.
1. Amnesia may be a sign of dementia

According to Dr. Restak, forgetfulness is a common aging process. Thus, it only warrants concern when it occurs frequently and involving items that ought to be commonplace. For instance, if you routinely lose track of details like your address, name, or family members’ names. He adds that while this is a typical aging symptom, it might not always indicate dementia.
2. Or aphasia

The term “aphasia” describes a problem of comprehension and communication. That is, a person’s capacity for speaking, writing, and reading could deteriorate. On a daily basis, this could appear to be someone who mispronounces a word or has forgotten what it means. Dr. Restak points out that this could not be a reliable indicator of dementia either. Why then include them? The solution is easy to understand. Diseases and people have a significant characteristic. Like diseases, we vary from case to case. No condition fits neatly into a box or checklist, and some symptoms may apply to some people but not to others. Rather, diseases and humans have certain characteristics that may fall into one category but not another. Consequently, even though these dementia symptoms might not apply to everyone, they can significantly help some people learn how to deal with and manage the condition.
3. Appropriate Indices of Dementia: Agnosia and Apraxia

One illness that affects the senses is anemia. It makes it impossible to identify well-known individuals or locations. This can be experienced by touch, taste, smell, sound, or sight. Among the instances are failing to identify a family member, house, or preferred destination for a Saturday excursion. Aphasia, on the other hand, is the final of the four symptoms of dementia and manifests itself when performing routine actions like brushing your teeth. Muscle function and strength are affected by the illness. Although apraxia can cause a person to forget to brush or even have difficulty holding the toothbrush, Dr. Restak cautions that the condition goes far deeper than that. When someone has apraxia, they frequently are unable to “tie all the actions together” or perform them in the right sequence. “An individual suffering from apraxia might be able to identify and even name a toothbrush and toothpaste, but they might not be able to perform the simple act of pressing toothpaste onto the toothbrush.” He composed. “All the muscle parts are there, but they are not able to work together.” Individuals in advanced phases could also find it difficult to take a shower or get dressed.Restak wrote in How to Prevent Dementia that “many, if not all, expressions of Alzheimer’s can be explained by reference to the four A’s.”
4. Alzheimer’s versus dementia
The title of the book is Dementia Prevention. Still, Dr. Restak makes several allusions to Alzheimer’s. This is due to the long-held belief that the two illnesses are very similar. While this is accurate, there are a few significant distinctions between the two, and it turns out that one frequently leads to the other. In general medicine, the term “dementia” refers to brain changes brought on by aging, illness, or trauma. the term used to describe a collection of symptoms that impair a person’s capacity to operate and carry out daily tasks. Conversely, Alzheimer’s is more common in the old and senior population and frequently results in dementia.
5. Having a Conversation with an Expert
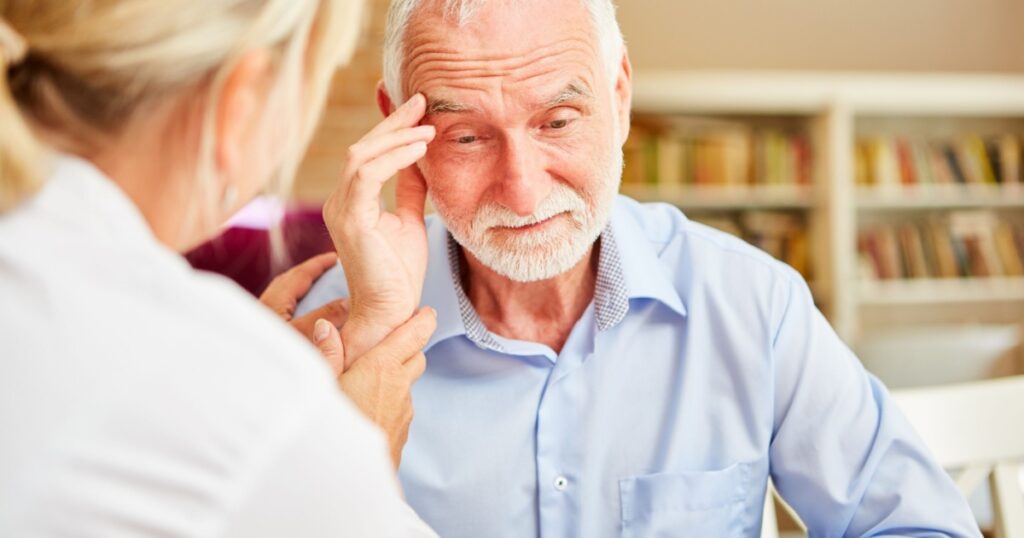

It’s advised to get in touch with a medical expert right away if you believe someone you know is showing dementia symptoms. They will have a better understanding of your symptoms and be able to conduct tests that will help determine the exact cause. But the discussion may also be frightening, awkward, and emotionally charged. There are a few things one can do to facilitate a more seamless communication. First, make sure everything is quiet, peaceful, and devoid of distractions like the TV. After that, get ready for an emotional roller coaster. Just provide the facts, but do so in a kind and perceptive manner. Summarize the important points in brief phrases and words. Permit the other individual to finish speaking. It might also be advisable in some circumstances to enlist expert assistance. For example, you can probably get emotional support, resources, and sometimes even medical guidance about what’s ahead from a religious leader, a primary care physician, or a certified therapist. In any case, the first step to learning to live with and conquer the obstacles brought on by dementia is being aware of its symptoms.
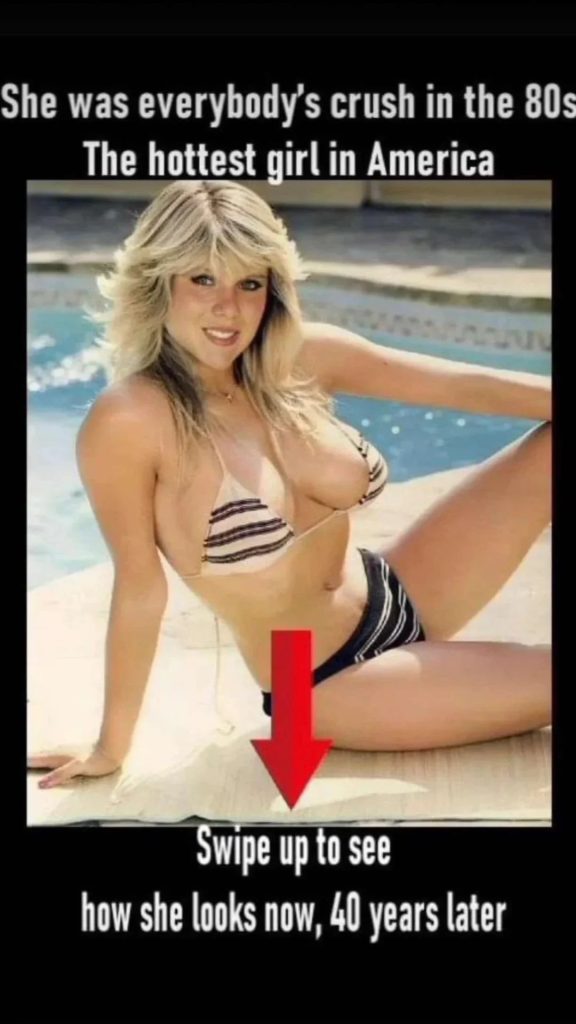
This 80s icon transitioned from modeling to music. Here’s how she looks four decades later.
Samantha Fox, born on April 15, 1966, in Mile End, London, England, grew up with a deep passion for the performing arts.




Leave a Reply