Trypophobia is a relatively lesser-known psychological phenomenon characterized by an intense aversion or fear of clustered patterns of small holes, bumps, or irregular shapes. While not officially recognized as a distinct mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), trypophobia has gained attention in recent years due to its prevalence and the emotional distress it can cause in individuals who experience it.
People with trypophobia often react strongly to images or objects that exhibit repetitive and closely packed small holes, such as lotus seed pods, honeycombs, or certain types of coral. The term “trypophobia” itself is derived from the Greek words “trypo,” meaning “hole,” and “phobia,” indicating an irrational fear. It’s important to note that trypophobia is not limited to specific shapes or textures; it encompasses a wide range of stimuli, and triggers can vary from person to person.
The fear response associated with trypophobia may manifest as feelings of discomfort, anxiety, nausea, or even panic attacks. Some individuals may go to great lengths to avoid situations or objects that could trigger their trypophobia, impacting their daily lives. While the exact cause of trypophobia remains unclear, researchers speculate that it may be linked to evolutionary factors, as some dangerous animals and plants exhibit similar patterns in nature.
Social media and the internet have played a significant role in popularizing trypophobia, with numerous online communities sharing images and discussions related to this phenomenon. The widespread dissemination of trypophobic triggers has led to increased awareness and recognition of this condition. However, it’s crucial to approach the topic with sensitivity, as exposure to triggering images can genuinely distress individuals who experience trypophobia.
Despite its prevalence, trypophobia remains an area of ongoing research, and professionals in psychology and psychiatry continue to explore its origins, manifestations, and potential treatments. Understanding trypophobia can contribute to more compassionate and informed discussions about mental health, promoting empathy and support for those who grapple with this unique fear.
Our thoughts and prayers go out to Jennifer Garner for her tragic loss
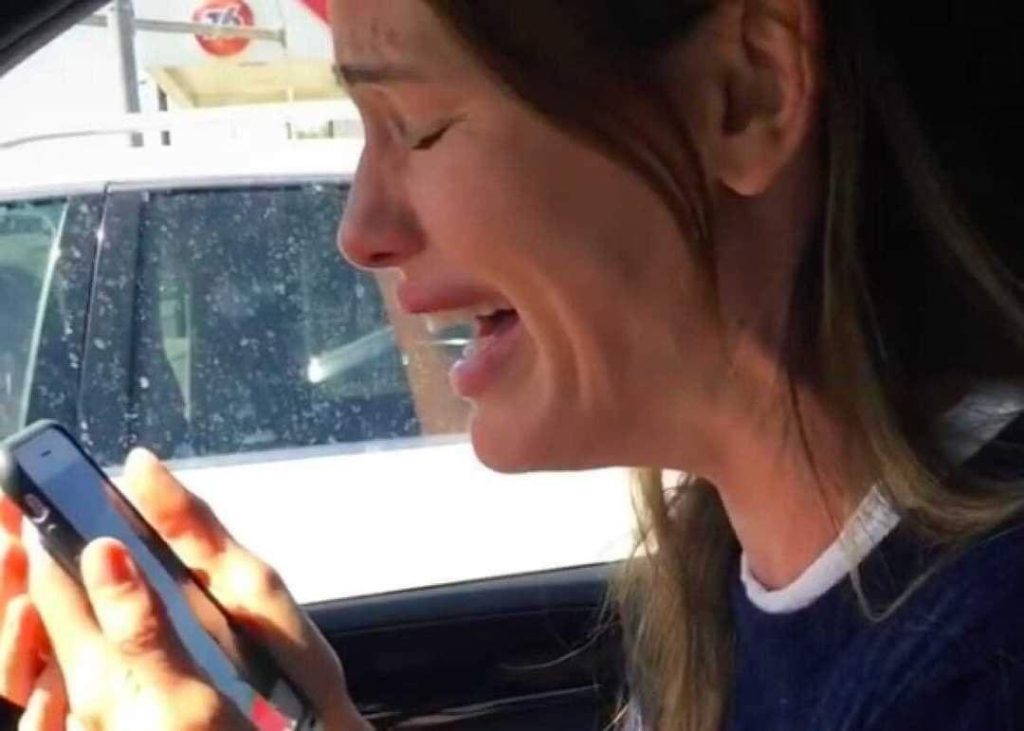

Jennifer Garner has had a successful career in Hollywood, but she has also stayed close to her parents.
The actress wrote on social media on Monday that her dad had died. He was 85 years old.
William John Garner was Jennifer Gardner’s dad. Who was he?
KBTX News 3 says that William John “Billy” Garner went to Texas A&M University and got his Bachelor of Chemical Engineering in 1961 and his Master of Chemical Engineering in 1976.
Stephen Garner was the dad of Jennifer Garner, Susannah Kay Garner Carpenter, and Melissa Garner Wylie.
Pat Garner, their mother, was his wife for almost 60 years.Jennifer wrote a blog post on January 1, 2024, to celebrate her parents’ 59th wedding anniversary.
“Happy 59th wedding anniversary to my loving and sweet parents!” “Thank you, Mom and Dad, for making sure my sisters and I had a safe and happy childhood,” she wrote.
She was born in Texas and grew up in Charleston, West Virginia.
The Hindustan Times says that William worked for Union Carbide as a chemical engineer.
What killed William John Garner?
“My dad died in peace on Saturday afternoon.” When he left, we were with him and sang “Amazing Grace.” Did we carry him across or scare him away? That’s a good question. “The death of an 85-year-old man who lived a healthy, happy life is not a tragedy, but I know that grief is inevitable and can come up at any time,” she wrote.
“Today is a day to be thankful,” she said.
“We are thankful for Dad’s kind nature and quiet strength.” For the way he teased with a sly grin and made up the part of the all-in, always-patient girl dad. He has a strong work ethic, is a good leader, and has faith.
But Jennifer did say that William was treated at Charleston Area Medical Center and City of Hope. She did not say what killed William.
“We want to thank the medical staff at Charleston Area Medical Center and City of Hope.” Your care made Dad’s life longer and gave him more time to do the things he loved, like being with his daughters and grandchildren, cheering for his beloved Aggies, being in charge of a boat, and most of all, being next to our mom, his wife of 59 years.
My sisters and I will never get tired of talking about how great my dad was, so please bear with us. For now, I’m sharing these memories to show how grateful I am for the kind and smart man, father, and grandfather he was, as well as the loving legacy he left behind.
Patricia Ann Garner is Jennifer Garner’s mom. Who is she?
Southern Living talked to Patricia about her family history. She grew up on a farm near Locust Grove, Oklahoma.
Harvey Newton English and Violet Margaret Sayre English bought the farm in 1936, during the Great Depression. Patricia was born in 1938, two years after her mum and dad moved there.


Leave a Reply