A group of researchers from the University of Nevada-Reno discovered that coffee grounds can be used as biodiesel, and quite possibly in the near future, your car fumes will smell like a cup of freshly brewed cappuccino. But that very first cup of coffee that fuels most of us in the morning may not be the best way to start your day. In fact, doctors believe the best time to enjoy your cup of java is mid- to late-morning, between 9:30 a.m. and 11:30 a.m.
We at Bright Side usually look forward to our first cup of coffee in the morning, but the effects it can have on your body when you drink it on an empty stomach can be a true wake-up call.
1. You may feel sleepier.

Coffee is a wake-up drink for many of us, but drinking it as soon as you roll out of bed may have the opposite effect. Caffeine doubles the levels of stress hormones and may lead to problems with sleep, which results in tiredness. If you start your day with a cup of cappuccino with sugar, you might feel sleepy again after a short period of time. This happens because our body produces insulin to offset the sugar, causing your blood glucose levels to drop, which results in a lack of energy and anxiety.
2. Your body may lose essential minerals more quickly.
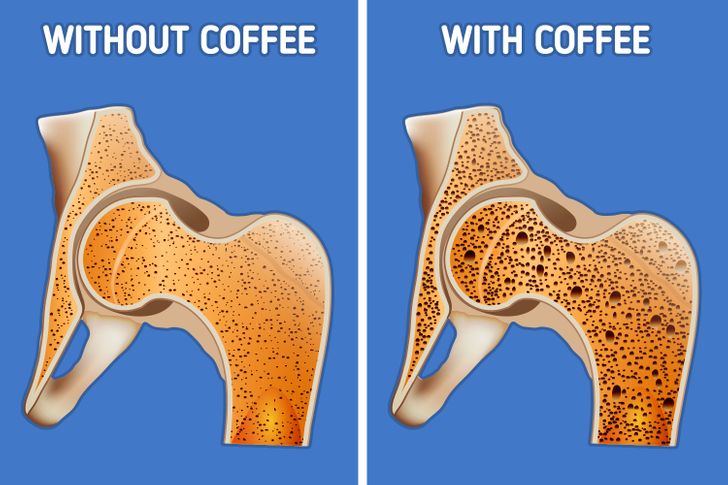
Having your regular dose of coffee early in the morning can cause you to lose many essential vitamins and minerals. It can sabotage the absorption of iron, magnesium, and B vitamins which are vital to our nervous system. Too much caffeine can also leach calcium from your bones, making them weak and brittle.
3. It may upset your stomach.

While your beloved beverage will help you to wake up in the morning, it may also give you the urge to use the bathroom more often. In fact, some medical experts even recommend drinking coffee as a way to prepare for certain exams. Coffee activates our nervous system, which in turn affects the colon and may cause diarrhea. Many people also like adding milk or cream to their morning cup of java, and because most of us have difficulty digesting lactose, it may cause stomach discomfort as well.
4. It may lead to weight gain.

Although black coffee may help you burn fat, it can also upset your healthy sleep patterns. When you don’t get enough sleep, you tend to feel hungrier and have more cravings for sweet snacks. Many coffee beverages, like popular sweetened blends, are packed with sugar and calories and might cause you to gain extra pounds.
5. It can worsen anxiety.
When you wake up in the morning, your stress hormones levels are usually at their highest. Because caffeine is a stimulant, it gives your body a jittery effect and can even trigger anxiety attacks for some people.
6. It can dry out your skin.
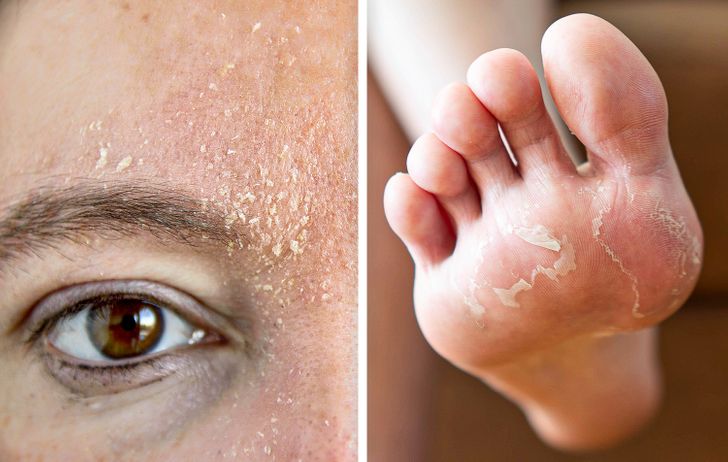
Because coffee makes you use the restroom more often, it dehydrates your body. When you become dehydrated, it’s harder for toxins to exit the body through your skin. This, in turn, dries the skin out and makes it more vulnerable to various problems, like premature wrinkles.
7. It may raise your blood sugar level.
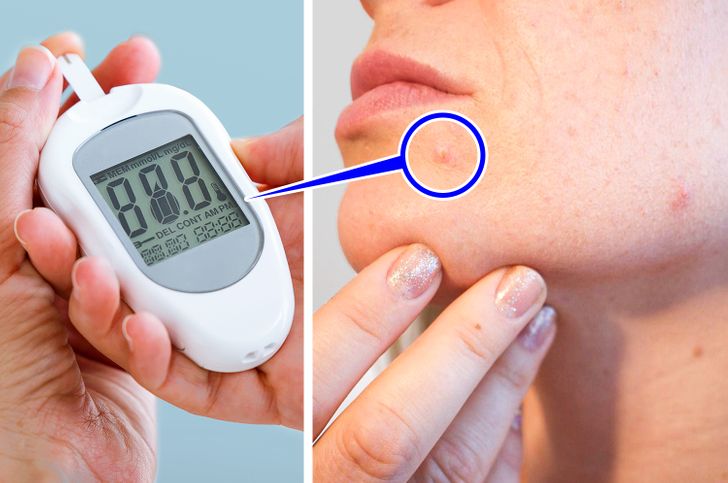
Your morning cup of coffee makes it harder for your cells to regulate blood sugar, which can lead to various diseases. High blood sugar, in turn, can lead to weight gain and even raise your risk of skin infections.
When do you usually drink your first cup of coffee? Have you noticed any of these side effects?
Preview photo credit Shutterstock.com
Entitled Landlord Raised Our Rent by $650 – We Had Enough and Taught Him a Costly Lesson

When our landlord hiked our rent by $650, it was the last straw. Living in a rundown apartment with a broken fridge and constant harassment pushed us to the edge. Determined to get revenge, we concocted a clever plan to make him regret his greed and teach him an unforgettable lesson.
Dennis here. Let me tell you about the time my wife, Amber, and I dealt with the landlord from hell while saving for our dream house. It’s been a rollercoaster, but we learned a lot along the way
So, picture this: Amber and I moved into this tiny, run-down apartment a little over a year ago.
We were pinching pennies, trying to save up for a place of our own. The apartment was our stepping stone. Small, but we made it work. Amber decorated the place with some second-hand finds and DIY projects. I swear, she can make anything look good.
The trouble started right from the get-go.

We met our landlord, Mr. Williams, during the lease signing. Now, this guy looked like he had stepped right out of a 1980s corporate villain movie. Slicked-back hair, smug smile, and a suit that screamed “I have power, and I love it.”
“Nice to meet you, Mr. Williams,” Amber said, ever the polite one.
“Likewise,” he replied, barely looking up from the paperwork. “Let’s get this done quickly. I have other matters to attend to.”
We went through the motions, signing here and there. And then, like an idiot, I mentioned my income.
Amber and I brainstormed over a couple of beers one night, sketching out ideas on a napkin. We needed something that would hit Mr. Williams where it hurt but couldn’t be traced back to us.
Then it hit us—smells. Horrible, pervasive, can’t-get-rid-of-them smells.
“Alright,” I said, leaning back with a grin. “We need tuna, rotten eggs, milk, and dead mice.”
Amber chuckled. “This is going to be epic.”
We removed the tuna, cleaned out the rotten eggs, scrubbed the milk stains, and disposed of the dead mice. The smell finally began to dissipate.
“Good riddance,” Amber said, wiping her hands. “I hope he learned his lesson.”
And there you have it. The story of how we turned the tables on our greedy landlord and got the justice we deserved. If you ever find yourself in a similar situation, remember: a little creativity and a lot of determination can go a long way!



Leave a Reply